Node Editor¶
A Node Editor presents an editable schematic or graph, displaying nodes and the connections between their attributes. It allows you to view, modify, and create new node connections.
You can see an example below
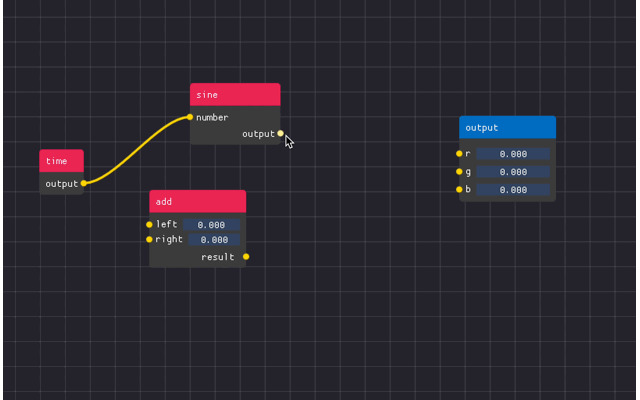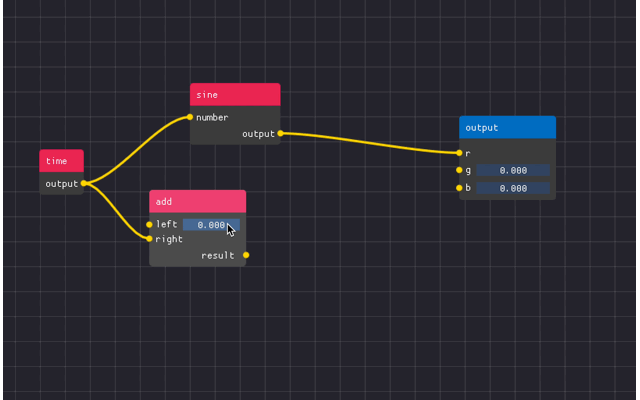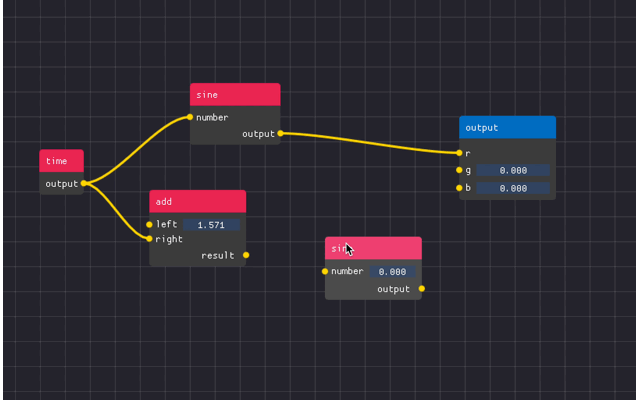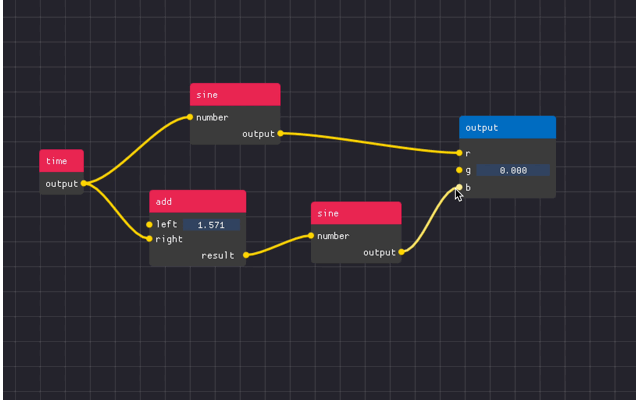
There are 4 main components
Node Editor - the area in which the nodes are located
Nodes - the free floating “windows” which contains attributes
- Attributes - the collections of widgets with pins to create links to/from.
Can be input, output, or static.
Links - the connections between attributes
Attributes can contain any UI Items. When a user clicks and drags a node’s attribute the node editor’s callback is ran. DPG sends the attributes’ tags through the _app_data_ argument of the callback.
It’s the developer’s responsibility to create the link.
Below is a basic example. You can grab an output pin and connect it to an input pin. You can detach a link by ctrl clicking the link and dragging it.
Code
import dearpygui.dearpygui as dpg
dpg.create_context()
# callback runs when user attempts to connect attributes
def link_callback(sender, app_data):
# app_data -> (link_id1, link_id2)
dpg.add_node_link(app_data[0], app_data[1], parent=sender)
# callback runs when user attempts to disconnect attributes
def delink_callback(sender, app_data):
# app_data -> link_id
dpg.delete_item(app_data)
with dpg.window(label="Tutorial", width=400, height=400):
with dpg.node_editor(callback=link_callback, delink_callback=delink_callback):
with dpg.node(label="Node 1"):
with dpg.node_attribute(label="Node A1"):
dpg.add_input_float(label="F1", width=150)
with dpg.node_attribute(label="Node A2", attribute_type=dpg.mvNode_Attr_Output):
dpg.add_input_float(label="F2", width=150)
with dpg.node(label="Node 2"):
with dpg.node_attribute(label="Node A3"):
dpg.add_input_float(label="F3", width=200)
with dpg.node_attribute(label="Node A4", attribute_type=dpg.mvNode_Attr_Output):
dpg.add_input_float(label="F4", width=200)
dpg.create_viewport(title='Custom Title', width=800, height=600)
dpg.setup_dearpygui()
dpg.show_viewport()
dpg.start_dearpygui()
dpg.destroy_context()
Selection Querying¶
You can retrieve selected nodes and links (and clear this selections with the following commands)
dpg.get_selected_nodes(editor_id)
dpg.get_selected_links(editor_id)
dpg.clear_selected_nodes(editor_id)
dpg.clear_selected_links(editor_id)
Node Attribute Types¶
The following constants can be used in the attribute_type argument for node attributes
Attribute |
mvNode_Attr_Input (default) |
mvNode_Attr_Output |
mvNode_Attr_Static |
Node Attribute Pin Shapes¶
The following constants can be used in the shape argument for node attributes
Shape |
mvNode_PinShape_Circle |
mvNode_PinShape_CircleFilled (default) |
mvNode_PinShape_Triangle |
mvNode_PinShape_TriangleFilled |
mvNode_PinShape_Quad |
mvNode_PinShape_QuadFilled |
Associated Items¶
mvNode
mvNodeAttribute
mvNodeLink